Physiologically Attentive User Interface for Robot Teleoperation: Real Time Emotional State Estimation and Interface Modification Using Physiology, Facial Expressions and Eye Movements
We developed a framework for Physiologically Attentive User Interfaces, to reduce the interaction gap between humans and machines in life critical robot teleoperations. Our system utilizes emotional state awareness capabilities of psychophysiology and classifies three emotional states (Resting, Stress, and Workload) by analysing physiological data along with facial expression and eye movement analysis. This emotional state estimation is then used to create a dynamic interface that updates in real time with respect to user’s emotional state.
Architecture
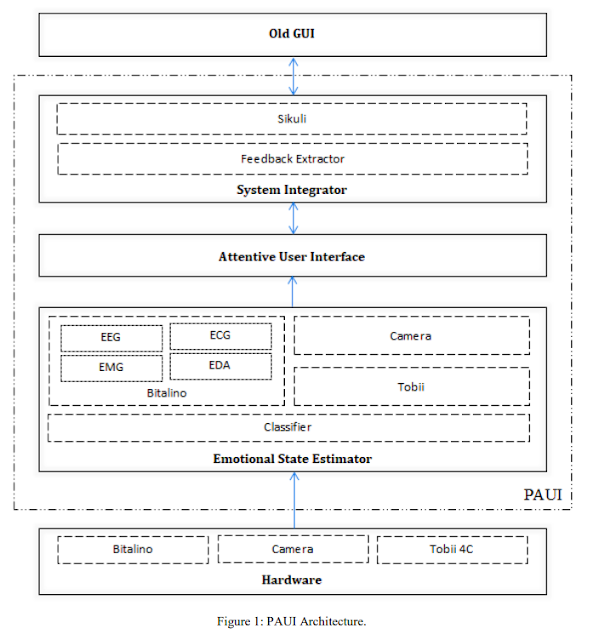
PAUI application’s architecture shown in figure 1 is divided into three sub modules that work alongside to achieve overall goal of creating Physiologically Attentive User Interface (PAUI) for robot teleoperation. The three sub modules are Emotional State Estimator (ESE), Attentive User Interface (AUI), and System Integrator (SI). ESE interacts with external hardware modules to extract covert and overt data of the user and process that for emotion prediction. This predicted emotional state is then fed to AUI that makes changes to its interface with respect to that. And SI is helping in filling the communication gap between old GUI and new PAUI. Moreover, communication between Hardware layer – ESE and ESE – AUI is one way, but between AUI – SI and SI – Old GUI is two way.
Emotional State Estimator (ESE)
This module is sub divided into 4 parallel threads: Bitalino thread extracts data at 1000 Hz for processing physiological signal; Camera thread processes camera images and extracts facial emotions at 15 Hz; Tobii thread extracts data at 90 Hz for tracking eye movements; and the Classifier thread runs at 2000 Hz that reads data from Bitalino, Camera, and Tobii thread, and performs emotion extraction and provides predicted emotion. Bitalino thread processes ECG signal for Heart Rate (HR), Heart Rate Variability i.e. Standard Deviation of Normal to Normal (SDNN) and Root Mean Square of the Successive Differences (RMSSD), and Frequency components i.e. Very Low Frequency (VLF from 0.0033 to 0.04), Low Frequency (LF from 0.04 to 0.15 Hz), and High Frequency (HF from 0.15 to 0.4 Hz). It processes EEG for Delta (0.5 – 3.5 Hz), Theta (3.5 – 8 Hz), Alpha (8 – 13 Hz), Beta (13 – 30 Hz), Gamma (30 – 45 Hz), and Engagement (Engagement = Beta / (Alpha + Theta)) suggested by McMahan et al. (2015). Processes EDA for Skin Conductance Level, Skin Conductance Response. And EMG is processed for Muscle Fiber Excitation (MFE).
Reference
Gaganpreet Singh, Sergi Bermúdez i Badia, Rodrigo Ventura, and José Luís Silva. (2018). Physiologically Attentive User Interface for Robot Teleoperation - Real Time Emotional State Estimation and Interface Modification Using Physiology, Facial Expressions and Eye Movements. Presented at the BIOSTEC 2018.


Comments